Understanding Forward and Reverse Logistics
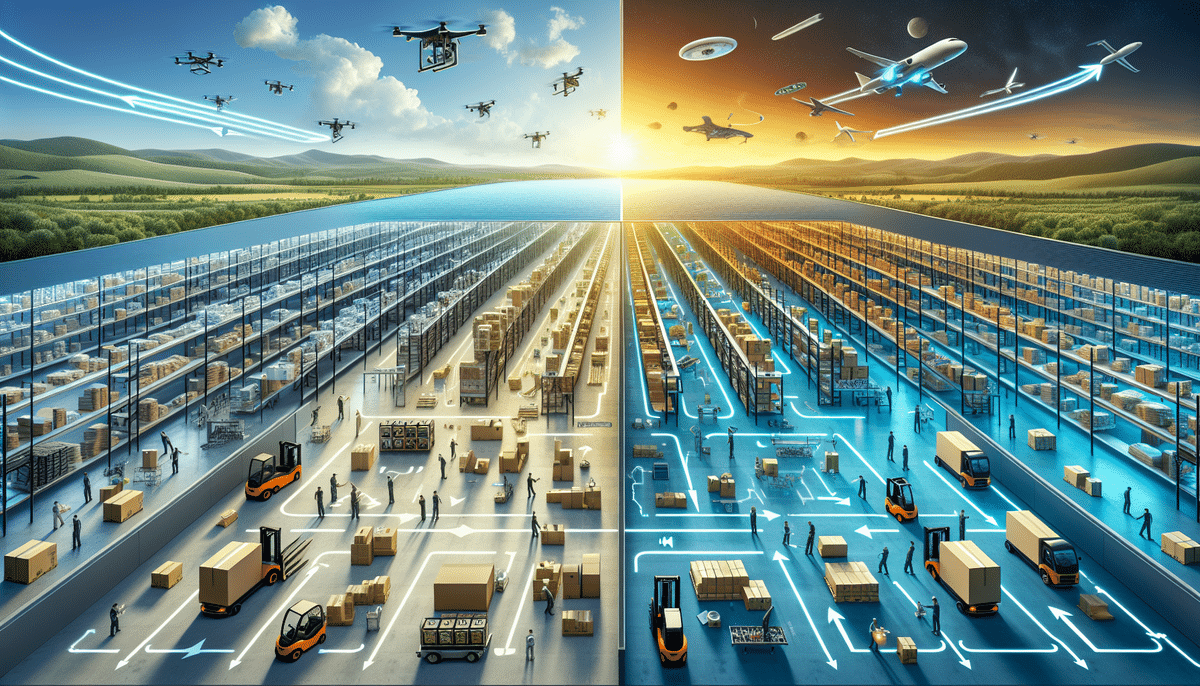
Logistics is a critical component of any business, encompassing the planning, implementation, and control of the movement of goods and services. It ensures that products flow efficiently from the point of origin to the point of consumption, a process known as forward logistics. Conversely, reverse logistics manages the flow of goods from the point of consumption back to the point of origin or disposition.
Forward Logistics: Definition and Significance
Forward logistics, also referred to as outbound logistics, involves managing the movement of goods and services from producers to consumers. Key activities include warehousing, transportation, and inventory management. The primary objective is to ensure timely delivery, minimize costs, and maximize profitability. According to a Supply Chain Digital report, efficient forward logistics can enhance customer satisfaction by reducing delivery times and ensuring product availability.
Challenges in Forward Logistics
Managing forward logistics effectively presents several challenges:
- Supply Chain Coordination: Coordinating with suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers requires seamless communication and collaboration.
- Technology Integration: Implementing advanced technologies such as automation and data analytics is essential for optimizing logistics processes.
- Sustainability: Businesses are increasingly focused on reducing their carbon footprint through optimized transportation routes and eco-friendly packaging.
- Cost Management: Balancing cost efficiency with service quality is a constant challenge.
Reverse Logistics: Definition and Significance
Reverse logistics, also known as aftermarket logistics, manages the return flow of goods from consumers back to producers for purposes such as returns, repairs, refurbishments, and recycling. The goal is to recover value, minimize environmental impact, and enhance customer satisfaction. As highlighted by the Inbound Logistics, effective reverse logistics can lead to significant cost savings and improved sustainability.
Challenges in Reverse Logistics
Reverse logistics involves unique challenges, including:
- Product Identification and Sorting: Efficiently identifying and categorizing returned products is crucial.
- Damage During Transport: Ensuring that returned goods are not further damaged during the reverse transportation process.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to recycling and disposal regulations requires meticulous planning and execution.
Key Differences Between Forward and Reverse Logistics
While forward and reverse logistics share similarities, they differ in several key aspects:
- Direction of Flow: Forward logistics moves goods from origin to consumption; reverse logistics moves goods from consumption back to origin.
- Primary Objectives: Forward logistics focuses on timely delivery and cost optimization, whereas reverse logistics aims to recover value and minimize waste.
- Product Types: Forward logistics handles new, finished goods, while reverse logistics deals with used, damaged, or obsolete products.
- Disposal Processes: Reverse logistics often involves recycling, refurbishing, or donating products.
- Required Expertise: Reverse logistics requires skills in managing returns, repairs, and regulatory compliance.
Strategies for Managing Forward and Reverse Logistics
Efficient Forward Logistics Management
Effective forward logistics management involves:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Developing a well-coordinated network that includes transportation, warehousing, and inventory management.
- Technology Adoption: Utilizing automation, data analytics, and artificial intelligence to enhance visibility and decision-making.
- Cost Optimization: Implementing strategies to reduce transportation and inventory costs without compromising service quality.
Effective Reverse Logistics Management
Managing reverse logistics efficiently requires:
- Systematic Approach: Establishing processes for product identification, quality control, sorting, and disposition.
- Reducing Returns Volume: Enhancing product quality and customer satisfaction to minimize returns.
- Collaborative Partnerships: Working closely with suppliers, customers, and logistics partners to handle returns and establish appropriate disposition methods.
The Role of Technology in Logistics
Technology plays a pivotal role in optimizing both forward and reverse logistics:
- Transportation Management Systems (TMS): Streamline transportation planning and execution.
- Warehouse Management Systems (WMS): Enhance warehouse operations through automation and real-time data.
- Inventory Management Systems: Improve inventory accuracy and turnover.
- Emerging Technologies: Blockchain, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT) are revolutionizing logistics by increasing transparency and efficiency.
Sustainable Practices in Logistics
Sustainability is increasingly integral to logistics management:
- Closed-Loop Supply Chains: Systems where materials are recovered, recycled, and reused, reducing waste and conserving resources.
- Eco-Friendly Packaging: Utilizing recyclable and biodegradable materials to minimize environmental impact.
- Energy-Efficient Transportation: Adopting energy-efficient modes of transportation and optimizing routes to reduce carbon emissions.
Case Studies: Successful Logistics Strategies
Amazon's Logistics Network
Amazon has developed an extensive logistics network that enables rapid delivery to customers, often within hours of order placement. Their investment in automation and advanced data analytics has optimized inventory management and transportation, resulting in high customer satisfaction levels [Forbes].
Nike's Closed-Loop Supply Chain
Nike has implemented a closed-loop supply chain by recycling used shoes and incorporating recycled materials into new products. This initiative not only minimizes waste but also promotes sustainability and resource conservation [Nike Sustainability].
Future Trends in Forward and Reverse Logistics
The logistics industry is continuously evolving, influenced by technological advancements and changing market demands:
- Automation and Robotics: Increased use of robots and autonomous vehicles to enhance efficiency.
- Big Data Analytics: Leveraging data to improve supply chain visibility and decision-making.
- Artificial Intelligence: Implementing AI for predictive analytics and process optimization.
- Blockchain Technology: Enhancing transparency and traceability across the supply chain.
- Enhanced Sustainability: Growing emphasis on sustainable logistics practices to reduce environmental impact.
Conclusion
Forward and reverse logistics are vital for the seamless operation of modern businesses. While forward logistics ensures the efficient delivery of goods to consumers, reverse logistics focuses on value recovery and sustainability. Effective management of both logistics streams requires a comprehensive approach that leverages technology, fosters collaboration, and embraces sustainable practices. By optimizing logistics operations, businesses can enhance customer satisfaction, reduce costs, and contribute to environmental conservation.